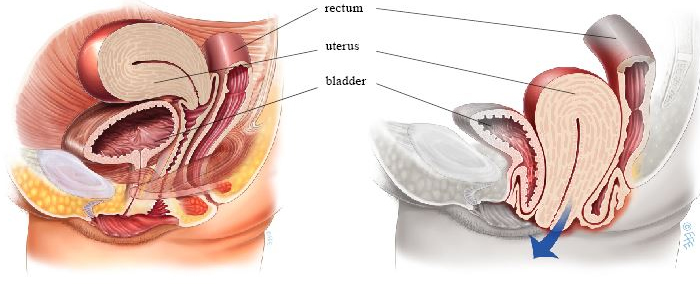
Vaginal hysterectomy is a surgical procedure in which the uterus is removed through the vaginal canal, without the need for abdominal incisions. It is considered a safe and effective method, particularly for women with conditions such as uterine prolapse, fibroids, adenomyosis, abnormal bleeding, or chronic pelvic pain. Vaginal hysterectomy has the advantage of faster recovery, less postoperative pain, minimal scarring, and reduced risk of infection compared to abdominal surgery.
The procedure is performed under general or regional anesthesia. The surgeon makes an incision in the upper part of the vagina to access and detach the uterus from surrounding structures, including ligaments, blood vessels, and the cervix if a total hysterectomy is being performed. The uterus is then removed through the vaginal canal. In some cases, additional procedures, such as removal of the fallopian tubes or ovaries, may be performed concurrently.
Vaginal hysterectomy is particularly suitable for women with a prolapsed uterus, where the uterus descends into the vaginal canal. It is also recommended when the uterus is of normal size and there are no significant adhesions from prior surgeries. Women with limited uterine mobility or very large fibroids may not be suitable candidates, in which case laparoscopic or abdominal approaches may be preferred.
Recovery after vaginal hysterectomy is generally quicker than abdominal hysterectomy, with most patients returning home within 1–3 days. Mild vaginal bleeding, pelvic discomfort, fatigue, and urinary changes are common during the initial recovery period. Patients are advised to avoid heavy lifting, sexual activity, and strenuous exercise for 4–6 weeks. Pelvic floor exercises may be recommended to strengthen muscles and aid in recovery.
Complications are rare but may include bleeding, infection, injury to the bladder or ureters, or vaginal cuff issues. Long-term follow-up is necessary to monitor healing and manage any menopausal symptoms if the ovaries are removed. Vaginal hysterectomy is particularly favored for its minimal invasiveness and cosmetic benefits, as it avoids external scars and allows a faster return to normal life.
Overall, vaginal hysterectomy is an effective, safe, and less invasive option for women requiring uterine removal. It is associated with shorter hospital stays, lower postoperative pain, and high patient satisfaction, making it an excellent choice when anatomically and medically appropriate.