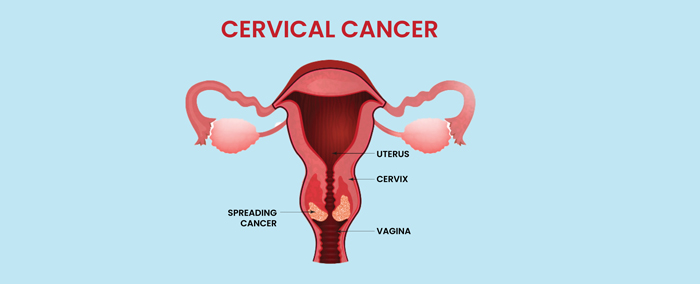
Cervical cancer develops in the cells of the cervix, the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. It is primarily caused by persistent infection with the Human Papillomavirus (HPV), a common sexually transmitted virus. While most HPV infections clear on their own, persistent high-risk strains can lead to precancerous changes that develop into cancer over several years. Because cervical cancer grows slowly, regular screening allows early detection and prevention.
The major risk factor is HPV infection, but additional risks include early sexual activity, multiple sexual partners, smoking, weakened immunity, long-term birth control pill use, poor genital hygiene, and lack of regular Pap smear tests. Socioeconomic factors and limited access to healthcare also contribute to higher cervical cancer rates in many regions.
Symptoms often do not appear in early stages. As the disease progresses, women may experience abnormal vaginal bleeding (especially after intercourse), bleeding between periods, foul-smelling vaginal discharge, pelvic pain, pain during intercourse, or bleeding after menopause. Advanced disease may lead to swelling of the legs, back pain, difficulty urinating, or blood in urine.
Cervical cancer is one of the most preventable cancers due to effective screening tests. Pap smear and HPV testing identify precancerous changes before they turn into cancer. When detected early, these abnormal cells can be treated easily through procedures such as cryotherapy, LEEP, or laser treatment.
Diagnosis of cervical cancer includes Pap test, HPV test, colposcopy, biopsy, and imaging tests for staging. Treatment depends on stage and may involve surgery (removal of cervix or uterus), radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these. Early-stage cervical cancer can often be cured, while advanced-stage cases can be managed effectively with combined treatments.
The HPV vaccine is a major breakthrough in preventing cervical cancer. It is recommended for girls and boys starting from age 9 to 14, offering long-term protection against high-risk HPV strains. Safe sexual practices, smoking cessation, good hygiene, and regular screenings further reduce risk.
Cervical cancer is highly treatable when detected early and largely preventable with vaccination and routine screening. Awareness, timely healthcare access, and preventive measures can significantly lower the incidence and improve outcomes for women worldwide.