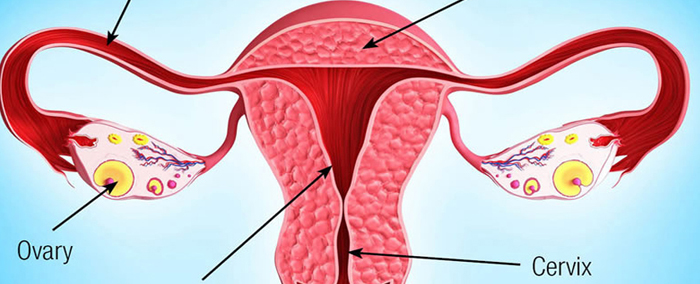
Ovarian cancer is one of the most serious gynecological cancers because it often develops silently and is usually diagnosed in its later stages. The ovaries are small reproductive glands responsible for producing hormones and releasing eggs. When abnormal cells in the ovaries begin to grow uncontrollably, they form tumors that can spread to nearby tissues and organs. Early symptoms are vague, making early detection challenging. However, improving awareness and timely evaluation can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
The exact cause of ovarian cancer is not known, but several risk factors contribute to its development. These include increasing age, family history of ovarian or breast cancer, inherited genetic mutations such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, infertility, endometriosis, obesity, and long-term hormone replacement therapy. Women who have never been pregnant or have menstrual cycles for many years without interruption may also have a slightly increased risk. Conversely, pregnancies, breastfeeding, and long-term use of birth control pills may lower risk.
Symptoms of ovarian cancer are often mistaken for digestive or menstrual issues. Common signs include bloating, abdominal or pelvic pain, heaviness, indigestion, frequent urination, loss of appetite, fatigue, and unexplained weight loss. When these symptoms occur daily for weeks, medical evaluation is important. In advanced stages, swelling of the abdomen due to fluid accumulation (ascites) is common.
Diagnosis involves pelvic examination, ultrasound, CT scans, MRI, tumor marker blood tests such as CA-125, and biopsy. Because ovarian cancer can spread quickly, timely diagnosis and staging are crucial for planning treatment. Treatment usually involves surgical removal of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, and sometimes lymph nodes or nearby tissues. After surgery, chemotherapy is typically required to eliminate remaining cancer cells. In some cases, targeted therapy or immunotherapy may be used depending on the cancer type and genetic profile.
Preventive techniques include genetic testing for high-risk women, healthy lifestyle maintenance, and risk-reducing surgery in selected cases. Women should pay attention to persistent abdominal symptoms and seek early gynecological consultation. Although ovarian cancer is challenging to diagnose early, advances in treatment, personalized therapies, and improved awareness offer better survival rates and improved quality of life for patients.