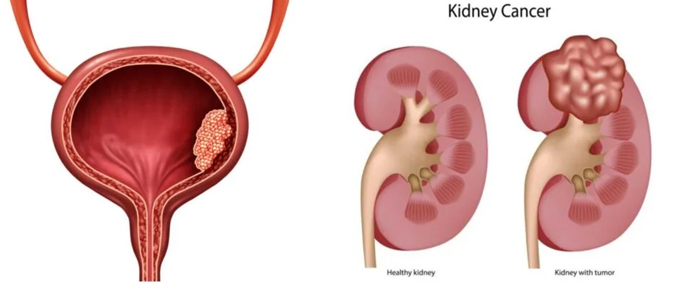
Kidney cancer, also known as renal cell carcinoma (RCC), is one of the most common urological cancers affecting both men and women. It begins in the small filtering units of the kidney, called nephrons, where blood is purified and waste is excreted. Kidney cancer typically develops silently and may not show symptoms until it reaches an advanced stage, making early diagnosis challenging but crucial.
Risk factors for kidney cancer include smoking, obesity, long-term high blood pressure, chronic kidney disease, family history, and exposure to certain chemicals. Smoking is one of the strongest contributors, increasing the risk by nearly double. Genetic conditions such as von Hippel–Lindau disease can also predispose individuals to RCC.
Early kidney cancer often does not produce noticeable symptoms. However, as the tumor grows, it may cause blood in the urine (hematuria), persistent lower back pain on one side, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, or a lump in the abdomen. Some individuals may experience fever, anemia, or high blood pressure due to hormonal changes caused by the tumor. Because these symptoms may appear late, regular health checkups and imaging are important, especially for individuals with risk factors.
Diagnosis usually involves ultrasound, CT scans, MRI, and urine and blood tests. A biopsy may be performed in select cases. The stage of cancer is determined based on tumor size, lymph node involvement, and spread to distant organs. Treatment depends on the stage and overall health of the patient. Early-stage kidney cancer is often treated through surgical removal of part (partial nephrectomy) or all of the kidney (radical nephrectomy). Minimally invasive laparoscopic and robotic procedures offer quicker recovery and fewer complications.
For advanced or metastatic kidney cancer, targeted therapies and immunotherapy have significantly improved survival rates. These treatments work by blocking cancer cell growth pathways or boosting the body's immune response to fight the tumor. Radiation and chemotherapy are rarely primary treatments for RCC, as kidney cancer cells respond poorly to them.
Prevention focuses on quitting smoking, maintaining healthy blood pressure, staying physically active, and managing weight. Early detection improves outcomes, and with modern treatments, many patients achieve long-term survival. Kidney cancer awareness and prompt medical attention for symptoms greatly enhance the chances of effective treatment.