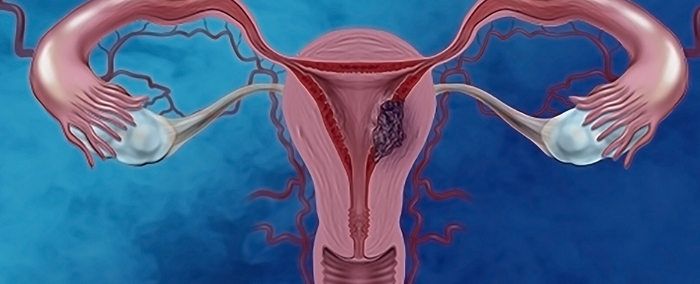
Uterine cancer, commonly known as endometrial cancer, begins in the lining of the uterus called the endometrium. It is the most common gynecological cancer and is frequently diagnosed in women who have reached or passed menopause. The disease develops when the endometrial cells grow uncontrollably, often due to hormonal imbalances, especially increased estrogen levels without adequate progesterone. Unlike many cancers, uterine cancer often produces early symptoms, making early detection more achievable.
Several risk factors contribute to uterine cancer. The strongest risk is prolonged exposure to estrogen. Conditions such as obesity, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), early menstruation, late menopause, diabetes, and infertility increase risk. Women who have never been pregnant are at a higher risk because pregnancy periods reduce lifetime exposure to estrogen. Hormone replacement therapy without progesterone, tamoxifen use, and family history of colon or endometrial cancer also play a role.
The most common and earliest symptom is abnormal vaginal bleeding, especially bleeding after menopause. Other symptoms may include heavy or irregular periods, spotting between cycles, pelvic pain, watery or blood-tinged discharge, discomfort during intercourse, and unexplained weight loss. Postmenopausal bleeding should always be evaluated immediately, as it is one of the most reliable warning signs.
Diagnosis involves pelvic examination, ultrasound, endometrial biopsy, dilation and curettage (D&C), and imaging tests such as CT or MRI to assess spread. Because symptoms appear early, many cases are diagnosed while still confined to the uterus, allowing effective treatment. Standard treatment includes surgical removal of the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes (hysterectomy). Depending on the stage and tumor type, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or hormone therapy may be recommended.
Preventive strategies involve maintaining a healthy weight, managing diabetes, treating PCOS, and ensuring balanced hormonal therapy when needed. Birth control pills and pregnancies may reduce risk by stabilizing hormone levels. Women experiencing persistent abnormal bleeding should seek medical evaluation promptly.
With timely detection, the prognosis for uterine cancer is often excellent. Most patients diagnosed early have high cure rates, and modern treatment plans offer improved outcomes and long-term disease control.