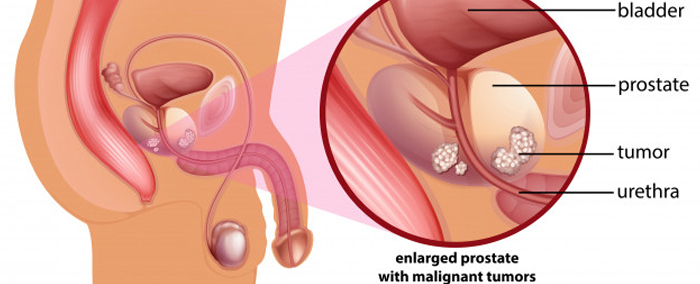
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting men, particularly those above the age of 50. The prostate is a walnut-sized gland located below the bladder and responsible for producing seminal fluid. Prostate cancer typically grows slowly, but some forms can be aggressive and spread rapidly, making early screening and diagnosis important.
Risk factors include age, family history, genetic mutations, obesity, and certain dietary habits. African and Asian ancestry may also influence risk patterns. Men with a father or brother diagnosed with prostate cancer have a significantly higher chance of developing the disease. Hormonal changes, particularly involving testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT), play a key role in prostate cell growth and cancer development.
Early-stage prostate cancer often produces no symptoms. When symptoms do appear, they may include difficulty urinating, weak urine flow, frequent urination at night, blood in urine or semen, pelvic discomfort, or erectile dysfunction. Advanced stages may cause bone pain, weight loss, or swelling in the legs due to lymphatic spread.
Diagnosis involves prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood tests, digital rectal examination (DRE), MRI, and prostate biopsy. PSA screening has helped detect prostate cancer at earlier stages, improving outcomes. However, elevated PSA levels can also be caused by infections or prostate enlargement, so proper evaluation is necessary.
Treatment depends on the stage and severity of disease. For early, slow-growing cancers, active surveillance may be recommended, involving regular PSA testing, imaging, and biopsies. Definitive treatments include prostatectomy (surgical removal of the prostate) and radiation therapy. Both approaches offer high cure rates for localized cancer.
Advanced prostate cancer may require hormone therapy (androgen deprivation therapy) to reduce testosterone levels, which slows cancer growth. Chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy may be used for metastatic disease. Newer treatments such as PSMA-targeted therapy have shown promising results in advanced cases.
Lifestyle factors also influence prostate health. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, omega-3 fatty acids, and low in processed foods may reduce risk. Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking contribute to overall wellness.
Prostate cancer is highly manageable when detected early. With advancements in diagnostics and treatment options, survival rates continue to improve, allowing many men to lead long, healthy lives after treatment.